
Summary
The harmony research, analysis and recording project is intended to teach students harmony structure and how to create harmonies for their musical ideas, or existing melodies.
Hookpad Beginner Tutorial – Part 3: Chords
Notes from Howard Goodall’s Harmony Video
| Cue | Notes |
| How do we know that we’ve found all of the harmonics to a note? How do we measure the difference? | “harmony is the intentional coming together of two or more sounds for a pleasant affect.” Western Harmony- drone follows the melody chord progressions are the life blood of western harmonies which move Whenever a note in the melody collides with drone notes, a chord progression is formed each chord is made of three notes, but within notes and chords there is a spectrum of other notes with deciding harmonics the basic chord we make up from harmonics is a triad tonic-dominant-subdominant are referred to as the primary triads discord/dissonancne is when notes intentionally put together arent supposed to fit together and belong to the wrong triads classifying dissonance has become more difficult with the passage of time churches called discord “the devil in music in the 17th cent.” only used to some dissonance-but still not all of it… passing/suspending notes can be forms of dissonance harmony makes music sound warmer and fuller several voices together rebel 2 |
Summary: I learned what defines a harmony, and about the different kinds of harmony used during progressions of western music.
Harmony Composition Terms and Definitions
- Harmony was not originally part of music until the middle ages and the renaissance
- Harmony sounds like it comes from some other plane of existence (to exaggerate a bit)
- Harmony in its simplest and oldest form in two notes playing at the same time
- A drone is a single note that you can sing any melody above. Bagpipes are an instrument that plays a drone.
- A drone is usually the tonic
- When people started to move the drone around, it was like the melody and the harmony were parallel lines. As the melody moved up, the drone moved up
- Triad – 3 notes that come together and create a chord
- Chord progressions are the backbone of western harmony
- People discovered the “hierarchy” of chords and created rules to go with these
- In one note, there are other hidden notes called harmonics
- Humans can only really pick out three or four harmonics
- Using the harmonics humans were able to make chords by finding the notes hidden in the harmonics
- In minor chords, the middle note is a half-step lower than in a major chord
- Polyphony is when you have a bunch of chords under the melody
- Polyphony – many “voices”
- Progression – a certain series of chords or notes that “work together” and sound good
- Tonic – the first note of a scale “home”
- Dominant – the fifth note of a scale that raises tension
- Passimezzo Antico – A chord progression that’s a variation of a double tonic. It was popular during the Italian Renaissance
- Passimezzo Moderno – “Modern half step” A chord progression that’s a variation of Passimezzo Antico. It divides the section in two and often uses a contrasting progression or section known as ripresi
- Dischord – a deliberate collision of notes that are meant not to sound “pretty”
- Dissonance – lack of harmony between notes “a clash”
- Passing Notes – notes that don’t sound “pretty” but are used a small number of times like they are just “passing through”
- Suspended Notes – dissonant notes being held for as long as possible and then finally moving at the last second
- 7th Chords – A regular triad chord plus the note seven steps above the first note
- Diminished Chords – A regular triad chord with the bottom note being moved up a step
- Augmented Chords – A regular triad chord with the last note being moved up a step
- Tonic (1 and 8 chords)
- Root note creates a feeling of resolution and stability
- Supertonic, Mediant, Submediant (2, 3, 6 chords)
- Moderate tension, useful for transitions
- Dominant, Subdominant, Leading Tone (4, 5, 7 chords)
- Create lots of tension to get to the tonic
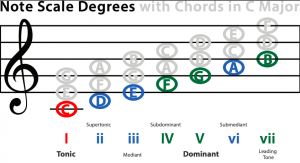
Mr. Le Duc’s Key of C Major Notes and Chords Chart (PDF)
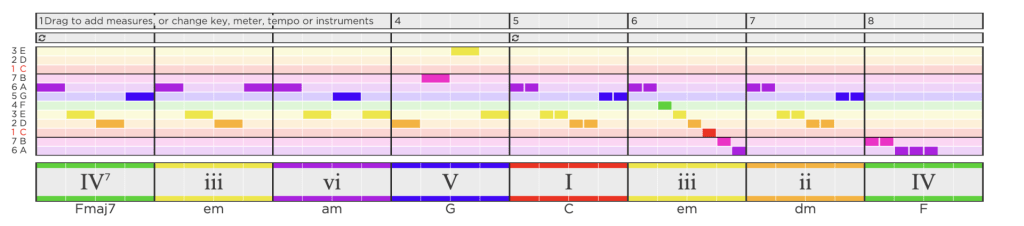
One of My Favorite (Chord Progressions) Harmonies

My Second HookTheory Chord Progression (Harmonies)
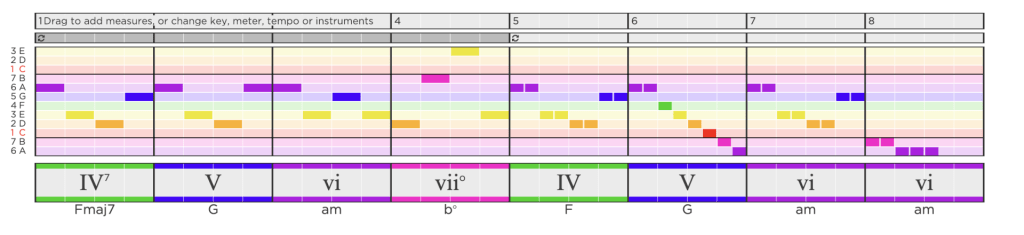
I like the chord progression I’ve written, because it follows the melody with little discord, allowing it to sound full in the short amount of measures available. I attempted raising tension at the fourth and seventh measures to follow the original melody, I released tension by gradually using lower-toned chords in the last two measures.
What I Learned & Problems I Solved
Before beginning this unit, I struggled ridiculously to understand the distinction between melodies and harmonies. I have a better idea of how to do that now, but I still think I need more time to put this simple task of recognizing distinctions into practice. From my updated understanding, melodies are made of a sequence of individual notes, while harmonies are made of chord sequences. Though the guiding principle I used for this project was a quote from Howard Goodall’s video which said that “-harmony is the intentional coming together of two or more sounds for a pleasant effect.”
Grammar and Spelling
Grammarly
Editor
Resources
- Assessment a Feedback
- General Music Composition Rubric (Google Doc)
- Hook Theory Tools and Tutorials
- Music Theory
- Free MIDI files midiworld.com/files/
- MIDI file of Beethoven’s Ode to Joy from his 9th symphony
- Coldplay Talk sample midi file
- MIDI and Music Notation Editors
- onlinesequencer.net – online
- flat.io – online
- noteflight.com – online
- MuseScore downloadable program
- GarageBand